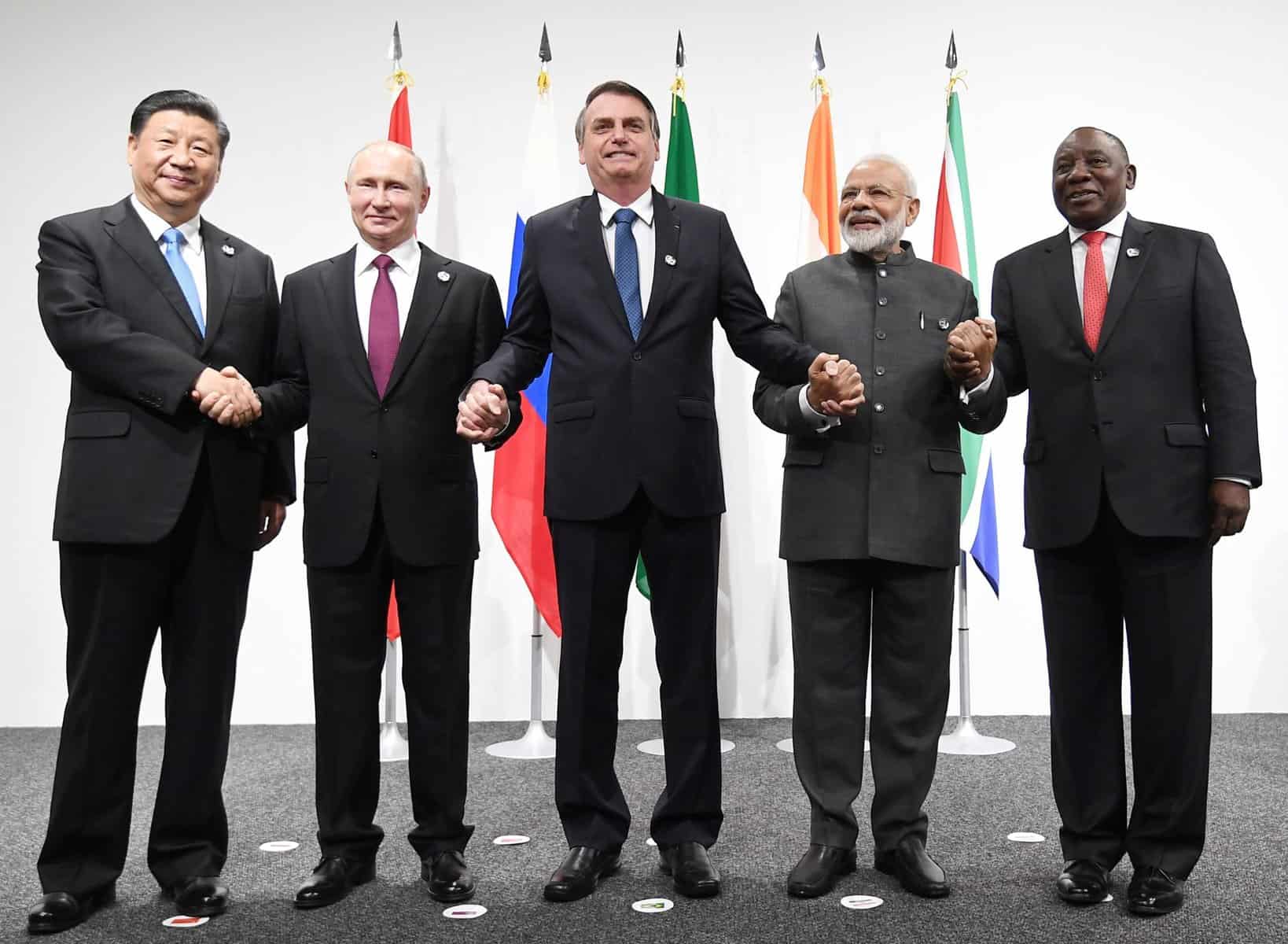

The Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi with the other leaders of BRICS nations, in Osaka, Japan on June 28, 2019.
BRICS De-Dollarization:
How the Bloc is Reshaping Global Finance in 2024
The concept of BRICS de-dollarization has gained significant momentum in 2024, marking a pivotal shift in the global financial landscape. As Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa collaboratively work to reduce their reliance on the U.S. dollar, they are not only challenging the longstanding dominance of the dollar but also paving the way for a multipolar financial system, a new vision of economy.
As a result, this strategic move by the BRICS nations aims to enhance economic sovereignty, mitigate vulnerabilities associated with dollar dependence, and try and promote a more balanced global economic order.
For nearly a century, the U.S. dollar has held an undisputed status as the world’s primary reserve currency, central to global finance, trade, and investment.
Consequently, in recent years, the geopolitical landscape has been shifting. Spearheaded by the BRICS bloc—Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa—there is a concerted effort to reduce dependency on the dollar.
This movement, known as de-dollarization, seeks to foster economic independence, protect national economies from external shocks, and establish a multipolar currency system less reliant on the dollar. Below, we explore the factors driving this shift, the strategies implemented by BRICS, and the implications for the future of the global financial landscape.
What is BRICS De-Dollarization?
The dollar’s dominance in global finance has deep historical roots. Following the Bretton Woods Agreement in 1944, the dollar was pegged to gold, establishing it as the world’s principal currency. Even after the U.S. abandoned the gold standard in 1971, the dollar’s influence continued to grow. Furthermore, the dollar accounts for roughly 59% of global reserves, down from 70% two decades ago, but it remains central to international trade, investments, and financial instruments.
As a result, the dollar’s primacy offers significant benefits to the U.S. It ensures constant demand for dollar-denominated assets, allows the U.S. to finance its deficits with relative ease, and enhances its geopolitical influence through monetary policy and sanctions.
However, this dependency also places other countries at risk, as they are directly affected by U.S. policy decisions and financial volatility.
For nations seeking greater economic sovereignty and resilience against external pressures, de-dollarization presents a strategic alternative, as in theory, it creates a more balanced economic strength between countries, without making them all co-dependent by USA economy.
Key Strategies Driving BRICS De-Dollarization
The BRICS nations collectively represent over 40% of the world’s population and account for nearly a quarter of global GDP. Their combined economic power makes them a formidable bloc, capable of challenging the dollar-dominated financial system. BRICS’ motivations for de-dollarization are varied, but some of the main drivers include:
Economic Sovereignty
By reducing reliance on the dollar, BRICS nations can protect their economies from U.S. policy fluctuations, especially interest rate adjustments by the Federal Reserve. High U.S. interest rates make dollar-denominated debt more expensive for developing countries, causing economic strain.
Protection Against Sanctions
Russia and Iran, key allies of BRICS, have faced extensive Western sanctions that limit their access to global financial markets. De-dollarization efforts aim to create a financial infrastructure that bypasses dollar transactions and mitigates the impact of sanctions.
Countering Dollar Dependency Risks
Dollar-centric trade means that fluctuations in the dollar’s value directly affect global commodities pricing. Shifting to alternative currencies helps BRICS nations reduce currency risk in their trade transactions, enhancing their financial stability.
Promoting a Multipolar Financial System
BRICS envisions a more balanced financial landscape, where global economic influence is distributed among various regions, currencies, and institutions rather than concentrated in a single country or currency.
Key Strategies and Mechanisms for De-Dollarization
BRICS has adopted a range of strategies to advance de-dollarization, from increasing bilateral trade in local currencies to establishing alternative financial institutions and payment systems. Some of the most prominent initiatives include:
Local Currency Trade Agreements: BRICS countries are increasingly conducting trade in national currencies rather than the dollar. For instance, India and Russia now settle much of their oil and energy trade in rupees and rubles, while China and Russia use the yuan for bilateral trade. As a result, this shift enables BRICS nations to reduce their reliance on the dollar, especially for essential goods like energy and raw materials.
Enhancing Gold Reserves as an Alternative Asset: To reduce their dependence on dollar assets, BRICS nations are bolstering their gold reserves. China and Russia, the world’s largest gold producers, are at the forefront of this trend, accumulating gold to hedge against currency fluctuations and potential sanctions. Collectively, BRICS holds over 20% of global gold reserves, and this strategy underscores their commitment to alternative assets.
Development of a BRICS Precious Metals Exchange: At the 16th annual BRICS Summit, member nations discussed creating a BRICS Precious Metals Exchange, a new platform for trading gold and other precious metals within the bloc. By establishing independent pricing standards, quality controls, and accreditation processes, this exchange could shield BRICS members from sanctions and create a stable trading environment outside of Western systems.
Alternative Financial Institutions: New Development Bank (NDB) and Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA): Established in 2014, the NDB finances infrastructure and sustainable development projects in local currencies, thereby reducing dependency on dollar-based funding. The Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA), a $100 billion reserve fund, provides BRICS countries with a financial safety net that allows them to address liquidity crises without relying on dollar-based entities like the IMF.
Creation of Alternative Payment Systems: Russia’s System for Transfer of Financial Messages (SPFS) and China’s Cross-Border Interbank Payment System (CIPS) provide alternatives to the U.S.-dominated SWIFT network. These systems enable secure cross-border transactions, reducing reliance on dollar-based transactions and offering BRICS countries a means to conduct trade without SWIFT.
The Role of Gold Reserves and Digital Currencies in BRICS’ De-Dollarization
As digital technologies advance, BRICS nations are exploring the potential of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) to support their de-dollarization efforts. For instance, China’s digital yuan enables cross-border transactions in real-time, bypassing the need for dollar conversions. CBDCs have the potential to streamline trade, lower transaction costs, and increase financial inclusion.
Additionally, the International Monetary Fund’s Special Drawing Rights (SDRs)—a basket of currencies including the dollar, euro, yuan, yen, and British pound—offer a diversified reserve asset. While SDRs currently represent a small fraction of global reserves, they may grow in importance as countries seek alternatives to traditional currency reserves, especially in times of economic uncertainty.
Challenges Facing the BRICS Bloc in De-Dollarization Efforts
Despite their progress, BRICS nations face significant obstacles in their de-dollarization efforts:
- Currency Convertibility and Liquidity Issues: Conducting trade in local currencies requires BRICS nations to hold each other’s currency in reserve, raising issues of convertibility and liquidity. India’s capital controls, for example, limit the movement of the rupee, complicating its use in international transactions.
- Institutional Differences Among BRICS Nations: The economic structures and priorities of BRICS members vary widely. For instance, China’s economy is much larger and more influential than that of other BRICS nations. This disparity complicates efforts to create a unified currency or monetary policy, as smaller economies may be reluctant to cede economic sovereignty to China.
- Adoption and Interoperability of Payment Systems: Alternative payment systems like CIPS and SPFS are gaining traction, but broader adoption is required for these systems to effectively replace SWIFT. Additionally, regulatory barriers and interoperability challenges hinder their widespread use in global trade.
- Global Demand for Dollar-Denominated Assets: The dollar remains deeply ingrained in global finance, and countries outside BRICS continue to hold substantial dollar reserves. The stability and liquidity of U.S. Treasury bonds make them attractive investments, even as BRICS promotes alternative assets.
Future Implications and the Path to a Multipolar Financial System
The gradual de-dollarization efforts by BRICS underscore a broader trend toward financial multipolarity. By diversifying reserve assets, promoting local currency trade, and developing independent financial systems, BRICS nations are challenging the long-standing dominance of the dollar.
As a consequence of this new order, a multipolar financial system is likely to emerge incrementally rather than through a swift replacement of the dollar.
Key developments shaping this future include:
- Expanding Influence of Alternative Currencies: The Chinese yuan is slowly gaining traction as a global currency, especially in Asia and Africa, where BRICS is focusing its trade partnerships. By expanding the yuan’s use in cross-border trade, China can enhance its influence while reducing dollar dependence.
- Growing Role of Gold and Digital Assets: BRICS nations’ focus on gold and CBDCs reflects a dual approach to de-dollarization.
- Gold provides a stable, universally recognized reserve asset, while digital currencies offer flexibility and transaction efficiency. This combined strategy strengthens BRICS’ resilience to economic shocks and potential sanctions.
- The Potential Impact of Geopolitical Alliances: BRICS has recently expanded to include Saudi Arabia, Iran, and other countries, broadening its reach and solidifying its influence. By bringing these key regional powers into its fold, BRICS is poised to further its de-dollarization objectives and promote a multipolar economic order.
- Building a Fairer Financial Landscape: The ultimate goal of de-dollarization for BRICS is to create a more balanced global financial system. By reducing dependency on any single currency, BRICS seeks to foster a fairer economic environment where developing nations have greater control over their monetary policy and economic future.
What should we expect from the future ?
BRICS’ de-dollarization efforts represent a fundamental shift in the global financial landscape, as developing nations collectively pursue financial independence from the U.S. dollar. Through a combination of local currency trade, enhanced gold reserves, alternative payment systems, and innovative digital solutions, BRICS is forging a path toward financial multipolarity. Although the dollar retains its dominance, the momentum behind BRICS’ initiatives suggests a gradual transformation of international finance.
As the global economy continues to evolve, the movement towards financial multipolarity may ultimately yield a more balanced and resilient financial order.
If you are interested in protecting your wealth from financial fluctuations through precious metals, take a look HERE at the best precious metals to IRA companies we are affiliated with.
Author

Ignazio Di Salvo
Founder
I have a background in Economics and Business Administration from Bocconi University and a formation in Digital Marketing. I am passionate about investments and I founded BestGoldMoney.com to help individuals make smarter decisions when investing in gold, silver, and other precious metals.
BestGoldMoney.Com
At Best Gold Money, we simplify the complexities of investing in precious metals. Our platform offers comprehensive insights, reviews, and reliable recommendations to help you make informed decisions about investments in precious metals.
We focus on providing valuable educational resources, expert analysis, and up-to-date information on the best practices for securing your financial future.
As part of our commitment to transparency, we participate in affiliate marketing programs, ensuring that we only endorse products and services we trust.