
What is a Gold IRA? Everything You Need to Know
If you’ve ever thought about safeguarding your retirement savings with something more resilient than stocks or mutual funds, chances are you’ve come across the term Gold IRA. But what exactly does it involve?
A Gold IRA is a specific type of self-directed individual retirement account that allows you to invest in physical precious metals, primarily gold coins and bullion, rather than traditional paper assets like stocks, bonds, or mutual funds. These metals are held in an IRS-approved depository, not in your home or bank safe deposit box.
What makes a Gold IRA compelling is its blend of control and long-term security. You’re investing in a tangible asset with a centuries-long track record of preserving wealth, while still benefiting from the tax advantages associated with traditional or Roth IRAs. In times of economic volatility, this combination becomes particularly attractive to investors seeking portfolio diversification and protection against inflation or currency devaluation.
This guide is designed to give you more than just surface-level definitions. We’ll walk you through how Gold IRAs actually function, the key regulatory rules you need to understand, potential pitfalls to avoid, and whether this type of investment aligns with your retirement objectives.

A Gold IRA is not your typical retirement account. While traditional IRAs are limited to paper assets like mutual funds, stocks, or bonds, a Gold IRA gives you the option to invest in something tangible: physical gold and other approved precious metals.
What makes it interesting is the control it gives you. This is a self-directed account, which means you decide what goes into it.
You can include gold bars, coins, and other IRS-approved metals, building a portfolio that reflects your own view of financial security.
We’ll also take a closer look at some of the leading U.S. companies currently offering Gold IRAs, examining what sets the most reputable providers apart from those that may pose higher risks or deliver subpar service.
If you’re considering rolling over an existing retirement account into a Gold IRA, we’ll walk you through how the process works. This is one of the most common funding methods, and when executed correctly, it can be done without triggering taxes or penalties.
From a tax perspective, Gold IRAs follow the same fundamental rules as standard traditional and Roth IRAs:
- With a Roth IRA, qualified withdrawals are tax-free.
- With a Traditional IRA, contributions may be tax-deductible, allowing for potential upfront tax savings while deferring taxes on investment gains.
To qualify as a Gold IRA under IRS guidelines, the account must hold physical precious metals—specifically bullion or coins that meet minimum fineness standards. You cannot simply invest in gold-related securities like mining stocks or ETFs; those belong in standard brokerage accounts. This distinction is what gives a Gold IRA its unique role in portfolio diversification.
Gold isn't the only eligible asset. These accounts can also include other IRS-approved metals like silver, platinum, and palladium. Depending on the custodian, some self-directed IRAs may also allow alternative assets, such as cryptocurrencies or structured annuities, but these fall outside the scope of a “Gold IRA” in the strict sense.
The key benefit? Diversification. With a Gold IRA, you’re allocating part of your retirement portfolio to hard assets that historically move independently of equities and fiat currencies. This can help mitigate risks tied to inflation, geopolitical tensions, or major market corrections—giving you broader protection over the long term.
We will also analyze in detail which are The best Gold IRA companies in the USA market and why you should, or should not, invest with one of them.
Furthermore, a Gold IRA rollover is another important process we will discuss in another article.
We also suggest you to take a look at our BLOG where you should find articles that will help you during your information research process.
These accounts are not limited to just gold. They can also include other precious metals like Silver, Platinum, Palladium and other various alternative assets such as cryptocurrencies or annuities, together with traditional investments like stocks and bonds. The strategic key point of this type of account is the diversification of the investments so that you can be protected from risks on one side, while collecting dividends from the other one.
Gold IRA Accounts
It’s important to note that Gold IRAs must be managed by IRS-approved custodians who specialize in self-directed retirement accounts.
These accounts are not typically available through mainstream brokerage firms, as the service model is highly specific. Custodians handle essential administrative tasks such as compliance with IRS regulations, asset storage arrangements, and reporting, making their role critical to the proper functioning of your Gold IRA.
If you're planning a rollover from an existing retirement account into a Gold IRA, we recommend reviewing our in-depth guide on the Precious Metals to IRA Rollover Process. It outlines the key steps, timeline, and regulatory requirements in a clear, actionable way.
Given their unique structure, many investors view Gold IRAs as a prudent strategy for diversifying retirement portfolios. They are often seen as a hedge against systemic financial risk, inflation, and currency devaluation, while offering the long-term wealth preservation that physical assets can provide.
On the other hands, investing in precious metals is not without risks. Market volatility, storage fees, and liquidity constraints are important factors to consider before making any allocation.
To make an informed decision, we strongly recommend reviewing the official IRS Guidelines for Gold IRAs, which define acceptable asset types, contribution rules, and storage requirements.
Finally, we’ve included a comparison of some of the leading Gold IRA providers in the U.S., to help you evaluate your options before choosing a custodian or opening an account.
Understanding How a Gold IRA Works
Some historical data
To fully understand how a Gold IRA works, it’s essential to consider both its legal origins and its operational framework.
The inclusion of physical precious metals in self-directed IRAs was made possible by the Taxpayer Relief Act of 1997. This legislation expanded the definition of eligible retirement assets, allowing individuals to incorporate tangible holdings, such as gold, silver, platinum, and palladium, into their long-term savings plans, provided those assets are held by IRS-approved custodians.
This was more than a technical amendment—it fundamentally reshaped how investors could approach retirement planning. For the first time, it became possible to directly own physical, IRS-compliant precious metals within a tax-advantaged account, offering an alternative to the volatility and systemic risks associated with purely paper-based investments.
Still, Gold IRAs are not universally suited to all investors. Some may be deterred by contribution limits, storage fees, or a general unfamiliarity with managing physical assets. However, for those seeking long-term stability and diversification, gold can provide a counterbalance to traditional equity-heavy portfolios, especially during periods of economic uncertainty.
To help you assess whether this strategy aligns with your financial goals, we’ve included a data-driven analysis below. It explores gold’s historical role in retirement planning and presents three model portfolio allocations, tailored to different risk tolerances and investment horizons.
The 3 types of portfolios when opening an investment account.
When investing in a Gold IRA, it's essential to understand the different portfolio strategies that can help diversify your retirement assets. Here are the three primary types of portfolios to consider:
- Conservative Portfolio
- This portfolio focuses on preserving capital and minimizing risk. It typically includes a higher percentage of traditional assets like bonds, cash, and a smaller portion of gold (around 10-15%).
- Ideal for investors nearing retirement who want to protect their wealth against market volatility.
- Balanced Portfolio
- A balanced portfolio aims to achieve steady growth while managing risk. It combines an equal mix of traditional assets (stocks, bonds) and gold, with gold making up about 20-30% of the total portfolio.
- This strategy is suitable for investors who want to enjoy growth potential while maintaining a level of security.
- Aggressive Portfolio
- An aggressive portfolio is designed for investors with a higher risk tolerance, focusing on maximizing returns. In this strategy, gold can make up 40% or more of the total portfolio, with the remaining assets invested in stocks, real estate, or alternative investments.
- Ideal for younger investors or those looking to capitalize on gold’s potential growth over the long term.
Choosing the right portfolio type depends on your financial goals, investment horizon, and risk tolerance. It's always wise to consult a financial advisor to tailor your portfolio to your specific needs.
Analyzing Gold Allocations (1972-2015)
To evaluate whether gold actually strengthens the performance of a retirement portfolio, an independent study analyzed market data spanning over four decades, from 1972 to 2015. The goal was simple: to compare how different portfolio allocations performed over time when incorporating varying levels of risk and asset diversification.
The analysis tested three model portfolios:
Conservative – 10% in U.S. stocks
Balanced – 35% in U.S. stocks
Aggressive – 95% in U.S. stocks
Each portfolio maintained the same selection of stocks but differed in allocation. The idea was to simulate how risk-tolerant versus risk-averse investors might build their portfolios in real life.
The following benchmarks were used to model performance:
Vanguard Total Market Index Fund (VTSMX) – data from 1993 to 2015
CRSP Market Decile 1–10 – covering 1972 to 1992
Vanguard Intermediate-Term Treasury Fund (VFIFX) – 1992 to 2015
Treasury Bills Risk-Free Return Benchmark – 1972 to 2015
In practical terms:
The moderate portfolio included 35% U.S. stocks, 60% 10-year Treasury bonds, and 5% in money market instruments.
The aggressive model leaned heavily toward equities, placing 95% in stocks.
The conservative model was heavily weighted toward treasuries, allocating 80% to bonds and only 20% to stocks and cash equivalents.
What emerged was a clearer picture of how asset mix influences performance. The variations in allocation affected both growth potential and volatility. This insight becomes critical when deciding whether to include precious metals like gold in a retirement plan.
Figure 1: Performance with Gold Allocation
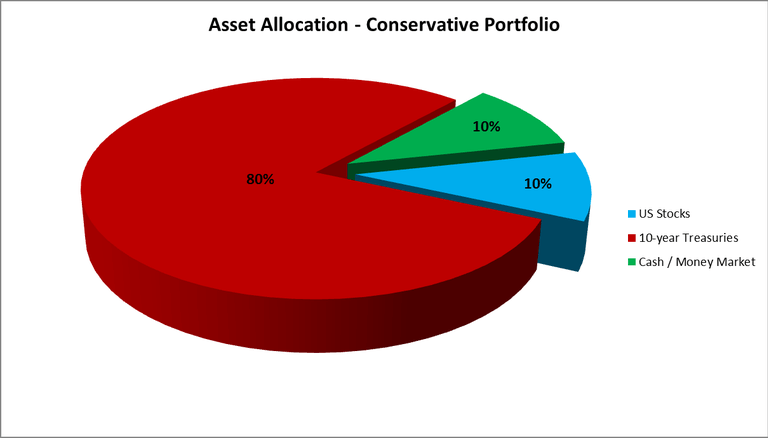
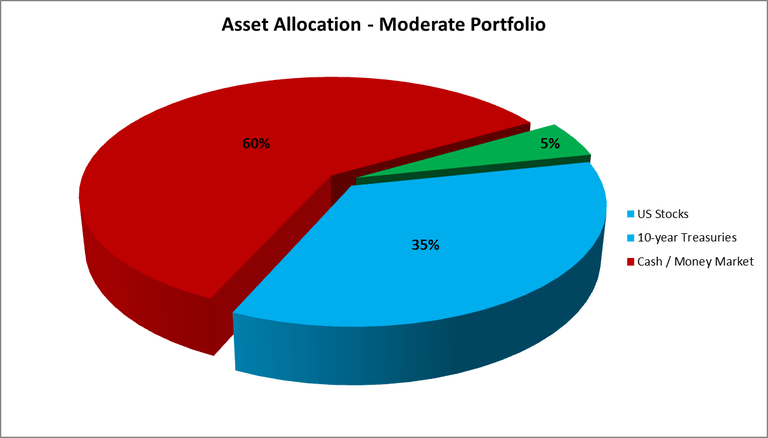
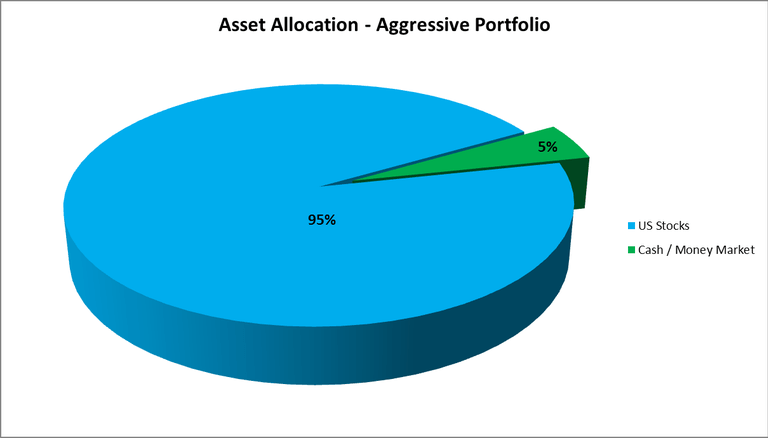
Results of the Study
Between 1972 and 2015, a moderate IRA portfolio that included a balanced mix of assets showed an average annual growth rate of 8.53 percent. If you had invested one million dollars at the start of that period, your portfolio would have grown to over 36 million dollars in 43 years.
This result alone is impressive. But what’s even more notable is how incorporating gold or other precious metals further strengthened the portfolio’s resilience and long-term value.
Even for conservative investors, dedicating a small portion of assets to gold can offer benefits beyond simple diversification. Historical data shows that gold tends to hold its value during times of crisis, making it an ideal hedge against inflation and market volatility. It doesn't just preserve purchasing power over time, it can amplify the overall stability of your retirement plan.
By adding gold to your IRA, you create the potential for not only greater returns but also more consistent protection in turbulent markets. That said, this isn’t a quick-win strategy. Physical gold is not designed to pay dividends or provide rapid gains. Its role is different: it protects and preserves.
If your goal is short-term yield or regular income through dividends, traditional market-based products might be more appropriate. But if you're building a portfolio for long-term security and stability, gold can be a smart, strategic component — especially in uncertain times.
Before deciding, it’s essential to weigh your time horizon, your tolerance for risk, and your expectations. A conversation with a qualified financial advisor is the best place to start.
Benefits of Investing in a Gold IRA

Investing in a Gold IRA can offer long-term protection and diversification, but it's not the right fit for everyone.Unlike traditional investments that may provide immediate returns or dividends, gold IRAs are designed to preserve wealth over time, particularly in uncertain economic periods.
Let’s explore the key advantages and disadvantages of investing in a Gold IRA to help you make an informed decision.
Pros of Gold IRAs
Pros
Cons
Are Gold IRAs Suitable for Me?
While most financial experts agree that diversification is a cornerstone of sound retirement planning, the decision to open a Gold IRA should be based on your personal financial objectives and risk profile. Precious metals are commonly used as a hedge against inflation, currency depreciation, and geopolitical instability. For some investors, allocating a portion, or even the entirety, of an existing IRA to gold or other approved metals can serve as a strategic move toward long-term preservation of wealth.
That said, the physical precious metals market operates under a different regulatory framework compared to traditional financial instruments like stocks or mutual funds. This makes it especially important to consult with a fee-only fiduciary financial advisor before making any major allocation. An impartial advisor can help ensure your investment choices are consistent with your overall retirement strategy, and assist in avoiding hidden fees, illiquid products, or overly aggressive sales tactics.
Steps to Open a Gold IRA
Opening a Gold IRA can be more complex than a traditional IRA due to IRS regulations and the physical handling of assets. However, many investors find the benefits, such as diversification and protection against inflation, worth the extra effort.
Here’s a simplified breakdown of the key steps involved in opening a Gold IRA:
1) Choose a Gold IRA Custodian:
To begin, you'll need to select an IRS-approved custodian. This company will set up your account and manage all the paperwork to make your IRA compliant with tax rules. Most custodians also handle the full process, from facilitating gold purchases to arranging secure shipment and storage.
While many investors rely on their custodian’s preferred gold dealer and storage partner, you are free to select your own, provided they are IRS-approved.
Make sure to research thoroughly and choose a provider that aligns with your expectations, fees, and investment approach.
2) Fund Your Gold IRA:
Once your account is open, it needs to be funded. You can do this by transferring money from an existing IRA or 401(k), sending a check, or initiating a wire transfer. This step activates the account and prepares it for the gold purchase.
Keep in mind that gold IRAs are subject to the same annual contribution limits as traditional IRAs. For 2024, the maximum is $7,000, or $8,000 for individuals over 50.
These limits apply whether you're starting a new account or adding to an existing one.
3) Select a Depository
You’ll then choose an IRS-approved depository to securely store your gold. Many custodians have established relationships with trusted storage facilities, which can simplify the process, but you're not obligated to use them.
It’s important to note that you cannot store the gold at home or combine it with other IRA-held investments such as mutual funds or stocks. IRS rules require that physical gold be kept in a secure third-party facility.
4) Purchase Gold:
Once the funds are available in your gold IRA account, instruct the custodian to buy gold on your behalf. You need to purchase from a dealer that sells IRS-approved gold, with Gold coins and bars being the most common choices. After the custodian places the order and sends payment to the dealer, the gold is shipped to the depository, where it is securely stored and recorded for tax purposes.
What Is the Difference Between a Gold IRA and a Traditional IRA?
When comparing a Gold IRA to a traditional IRA, it’s helpful to first understand what they have in common—before looking at what sets them apart.
Both account types share fundamental tax advantages. Contributions to Traditional IRAs, including those used to fund Gold IRAs, are often made with pre-tax income. This means your contribution may be tax-deductible, reducing your taxable income for the year. Any gains within the account grow tax-deferred, and you’ll only pay taxes when you begin making withdrawals in retirement.
Another point of similarity is that both Traditional and Gold IRAs can be structured as Roth accounts. In a Roth Gold IRA, you contribute post-tax income. While there’s no immediate tax deduction, qualified withdrawals, including both contributions and earnings, are completely tax-free in retirement.
This Roth structure is often favored by investors who expect to be in a higher tax bracket in the future, or who want to minimize their tax burden over the long term.
It’s important to note that contribution limits and income eligibility rules still apply, especially for Roth IRAs. For example, high-income earners may face phaseouts or require a backdoor Roth strategy.
In short, the key distinction lies not in the tax structure, but in the asset composition. Traditional IRAs hold paper assets such as stocks, bonds, or mutual funds. Gold IRAs, on the other hand, hold IRS-approved physical precious metals, offering a tangible hedge against market volatility and inflation.
Gold IRA Storage Options

When you invest in a Gold IRA, one of the most important decisions you’ll make is how and where to store your precious metals. The IRS has strict rules in place to ensure that physical assets like gold, silver, platinum, and palladium are stored safely and securely. Let’s take a closer look at your options.
IRS-Approved Precious Metals Depositories in the U.S.
To be compliant with IRS regulations, all metals in a Gold IRA must be stored in approved depositories managed by qualified professionals. These facilities are specifically authorized to handle high-value precious metals under secure and audited conditions.
Here are the six main IRS-approved depositories in the United States:
- Delaware Depository
- Brinks Security
- HSBC Bank USA
- JPMorgan Chase Bank North America
- Scotia Mocatta
These institutions provide robust protection for your assets, and many also offer international storage options in global financial centers like London, Singapore, Toronto, Zurich, and Hong Kong.
Offshore Storage vs. Local Storage
Some Gold IRA companies allow investors to store their metals outside the U.S. Offshore storage can provide an extra layer of protection against domestic risks such as political instability or economic disruptions. However, it often comes with additional fees and legal considerations.
Common offshore storage locations include:
- Brinks (London)
- HSBC (London, Zurich, Singapore, Hong Kong)
- JPMorgan Chase (London, Singapore)
- Scotia Mocatta (Toronto)
Offshore storage can be a smart diversification strategy, especially for those concerned about keeping all their wealth in a single jurisdiction.
Co-mingled vs. Segregated Storage
Co-mingled storage means your metals are stored alongside those of other investors. This is the more affordable option but does not give you individual ownership over specific coins or bars.
Segregated storage provides a higher level of security. Your metals are stored separately, under your name, in a clearly designated section of the vault.
Although this option typically comes with higher fees, it ensures you retain full legal ownership and easy auditability of your specific assets.
If you're serious about protecting your retirement savings, segregated storage is generally the preferred choice.
Can You Store Gold IRA Metals at Home?
No. Storing Gold IRA metals at home is strictly prohibited by IRS rules. While some companies falsely advertise home storage options, doing so can lead to tax penalties, legal issues, and even disqualification of your IRA. Only IRS-approved custodians and financial institutions are legally allowed to store IRA metals.
Always verify the legitimacy of any storage offer and stay away from schemes that promise shortcuts or loopholes.
What Metals Can You Store?
Not all metals are eligible for IRA investment. The IRS has set specific purity standards for metals to be approved into IRAs:
- Gold: 0.995 or higher
- Silver: 0.999 or higher
- Platinum: 0.9995 or higher
- Palladium: 0.9995 or higher
Collectors' coins or rare metals generally do not meet these requirements and are not allowed in IRAs. You can read more about this subject in this article. By understanding your storage options and the regulations, you can make informed decisions to secure your gold IRA investments. Always follow IRS guidelines to avoid penalties and ensure the safety of your assets.

Gold IRA Rules and Regulations
The IRS has established strict rules for gold IRAs to ensure compliance and security. Here’s a simplified overview of these regulations:
Account Administrator Rules
To set up a gold IRA, you must use an IRS-approved administrator. It’s important to note that you cannot buy gold or other precious metals with your IRA funds personally, as it is forbidden. Instead, your IRA administrator will take care of all the transactions on your behalf: from purchasing to shipping, while insuring the precious metals in your account.
Storage Rules
You are not allowed to keep IRA-included coins or precious metals in your possession. If you do, the IRS will consider these metals as distributed and will impose penalties and taxes. Your custodian will store your metals in an IRS-approved third-party depository. You can request segregated storage for added security, even if this may incur in higher fees.
Tax Regulations and Contribution Limits
The annual contribution limit for self-directed IRAs in 2024 is $7,000, increasing to $8,000 for those aged 50 and above. If you withdraw from your IRA before age 59½, you’ll face income tax and a 10% penalty on the value of the metals withdrawn. Additionally, a 28% capital gains tax applies to any profits from the original cost basis.
Retirement Age Limits
You can’t access your gold IRA funds without a penalty until you reach age 59½. By age 70, you must begin taking regular distributions from your account.
Early Withdrawal Penalties and Exceptions
The IRS imposes a 10% penalty for early withdrawals but provides exceptions for specific circumstances, such as permanent disability, significant medical expenses, death, unemployment, education costs, and first-time home purchases.
Learn more about Gold IRA regulations on IRS official website.
Is a Gold IRA Right for You?
In this article, we explained to you in details why you should invest in Gold (or other precious metals) to IRA and which are the main rules. You can also take a look at this article we also wrote, to have a better insight about the pros and the cons of this type of investment.
Generally speaking, investing in a Gold IRA is a fantastic option to create wealth overtime, grow and diversify your portfolio while maintaining it far from risks.
Consequently, it can be seen as a good option to keep safe and secure a part of your asset. On the other hand, we must advise being careful before investing with Precious Metals to IRA companies.
There might be inner costs and charges. It is also important to say that gold does not create dividends and that its price can fluctuate with the market as well, even if generally less than stock markets. For this reason, we highly recommend you to seek advice from an investments' consultant before proceeding.
FAQ
A Gold IRA is a self-directed individual retirement account allowing investments in physical gold and other precious metals. It offers the same tax benefits as standard IRAs but requires an IRS-approved custodian to manage the assets.
Benefits include diversification, protection against market volatility, tax advantages, and potential for long-term growth.
Eligible metals include gold (0.995 purity), silver (0.999), platinum (0.9995), and palladium (0.9995).
- Open a self-directed IRA with an IRS-approved custodian.
- Choose a reputable precious metal's dealer.
- Fund the account through contributions, transfers, or rollovers.
- Purchase IRS-approved metals to be stored in an approved depository.
You can choose between co-mingled or segregated storage in IRS-approved facilities. Offshore storage is also available.
Costs include setup fees, storage fees, and custodial fees. These can impact overall returns.
Risks include higher fees, storage limitations, counterparty risks, and opportunity costs compared to other asset classes.
Gold IRAs must comply with IRS rules regarding custodians, storage, tax regulations, and contribution limits. Early withdrawals may incur penalties.
A rollover involves moving funds from one retirement account to another within 60 days, while a transfer directly moves funds between custodians without penalties or taxes.
Consider factors such as reputation, storage options, years in business, and compliance with IRS regulations.
Subscribe to get our FREE
GOLD IRA GUIDE
Articles on all your favorite subjects
Author

Ignazio Di Salvo
Founder
I have a background in Economics and Business Administration from Bocconi University and a formation in Digital Marketing. I am passionate about investments and I founded BestGoldMoney.com to help individuals make smarter decisions when investing in gold, silver, and other precious metals.